Using a Hydrological Model to Link Stakeholder Engagement with Groundwater Management
May 23, 2016
Journal Water
,
Ashok K. Chapagain ed.
8 vol.
,
no. 5
, pages 1-17
,
17 pp.
,
MDPI AG
,
Water EISSN 2073-4441 Published by MDPI AG
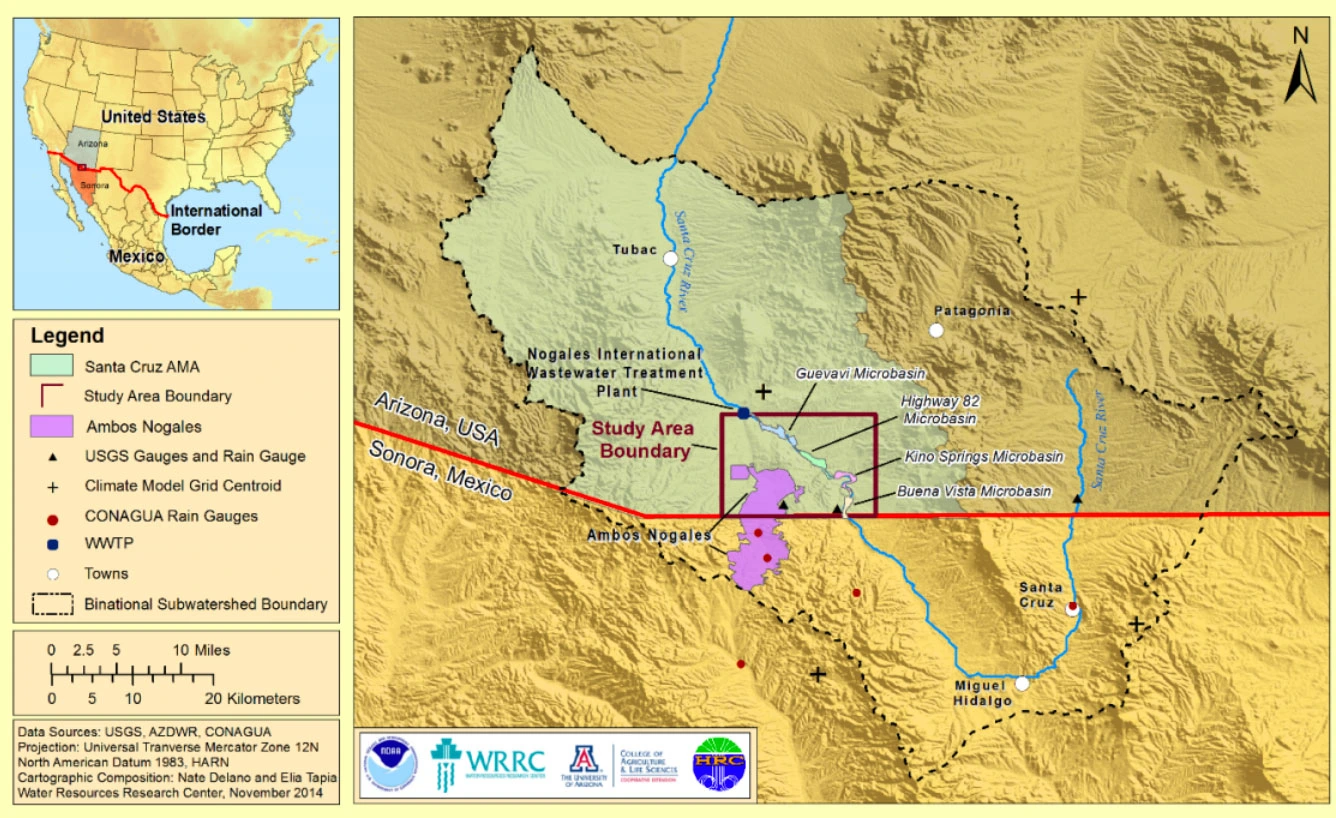
Stakeholder participation is a foundation of good water governance. Good groundwater governance typically involves the co-production of knowledge about the groundwater system. Models provide a vehicle for producing this knowledge, as well as a “boundary object” around which scientists and stakeholders can convene the co-production process. Through co-production, stakeholders and scientific experts can engage in exchanges that create system knowledge not otherwise achievable. The process involves one-way transfer of information, active two-way conversations, and integration of multiple kinds of knowledge into shared understanding. In the Upper Santa Cruz River basin in Arizona, USA, the University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center (WRRC) convened a project aimed at providing scientific underpinnings for groundwater planning and management. This project, entitled Groundwater, Climate, and Stakeholder Engagement, serves as a case study employing the first two stages of knowledge co-production using a hydrological model. Through an iterative process that included two-way communication, stakeholders provided critical input to hydrologic modeling analyses. Acting as a bridging organization, the WRRC facilitated a co-production process, involving location-specific and transferability workshops, which resulted in new knowledge and capacity for applying the model to novel problems.

